Abstract
Introduction: Up to 40% of newly diagnosed diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) will relapse after frontline rituximab, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone (RCHOP), with subsequent poor prognosis. Identification of patients (pts) at high risk of relapse early in the treatment can allow for development of risk adapted therapies to improve outcomes. Positron Emission Tomography scan after 2 cycles of therapy (PET2) has been evaluated as a predictor of relapse but study treatments were heterogenous and results were conflicting. A substudy of CALGB 50303 trial did not find association of PET2 response by Deauville Score (DS) with survival in RCHOP and DA-EPOCH-R treated pts. In the UK National Cancer Research Institute Prospective Study, DS of 5 on PET2 predicted worse progression free survival but not overall survival (OS) in RCHOP-21 and RCHOP-14 treated pts. Here we report impact of PET2 response on outcomes in two large independent, prospective cohorts of newly diagnosed DLBCL treated homogenously with two RCHOP-based regimens of similar efficacy.
Methods: Discovery was done in adult pts with DLBCL enrolled into a single arm phase 2 trial of lenalidomide plus standard RCHOP (R2CHOP) (MC078E, NCT00670358). The validation cohort comprised of adult pts with newly diagnosed DLBCL treated with standard RCHOP prospectively enrolled into the Mayo component of the University of Iowa/Mayo Clinic Molecular Epidemiology Resource (MER). Both MC078E and MER cohorts included patients who received at least 3-6 cycles of therapy and had a PET2. Pts who progressed on PET2 were excluded. End of treatment (EOT) PET was done 3-12 weeks after last cycle of therapy. The revised response criteria for malignant lymphoma (Cheson, et al 2007) was used to assess PET in MC078E. In MER, revised response criteria for malignant lymphoma (Cheson et al 2007) or Lugano classification was used, depending on era of diagnosis. Positive PET was defined as FDG uptake above background (Cheson 2007) or DS 4 or 5 (Lugano 2014). Study endpoints were event-free survival (EFS) and OS by PET2 status.
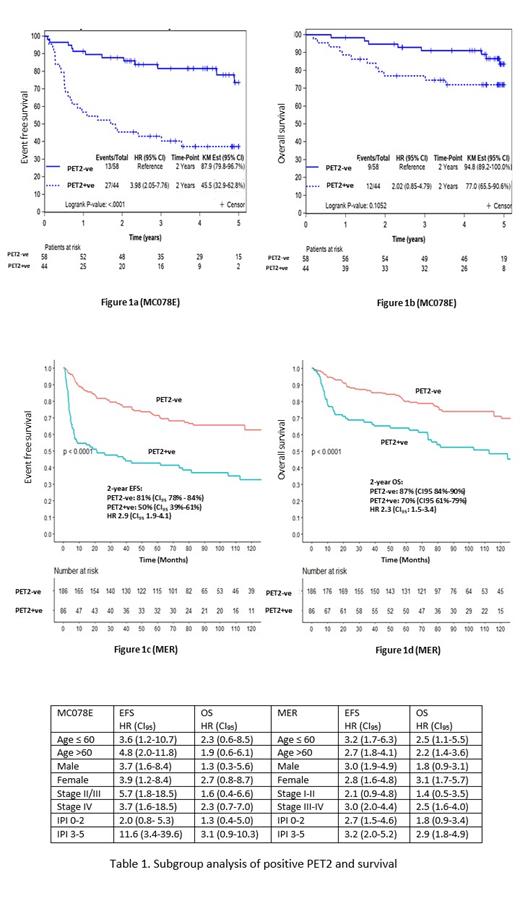
Results: Out of 118 pts treated on MC078E, 102 had PET2 (MC078E). The median age at diagnosis was 64 years (range 19-87), 61 (60%) were male, 89 (87%) had advanced stage disease, 46 (45%) had international prognostic index (IPI) of 3-5. 58 (57%) were PET2 Negative (PET2-ve) and 44 (43%) were PET2 Positive (PET2+ve). At EOT PET, 83 (81%) had -ve PET and 15 (15%) had +ve PET. Out of 44 PET2+ve pts, 15 remained +ve at EOT PET. Out of 58 PET2-ve pts, 56 had EOT PET available and all were -ve.
Out of 866 DLBCL pts enrolled into MER between August 2005 and June 2015, 621 were treated with RCHOP for 3-6 cycles and 272 had available PET2 (MER). The median age was 65 years (range 55-73), 152 (56%) were male, 174 (64%) had advanced stage, 103 (38%) had IPI 3-5. 186 (68%) were PET2-ve and 86 (32%) were PET2+ve. Out of 235 with EOT PET available, 182 (77%) had -ve EOT PET and 25 (11%) had +ve EOT PET. PET2+ve pts had higher odds of +ve EOT PET (OR: 17.4 (CI 95 8.3-40.0), p<0.001) and progression on EOT PET (OR: 4.3 (CI 95 1.9-10.2), p<0.001) in MER cohort. This analysis was not possible on MC078E as all PET2-ve had -ve EOT PET.
In MC078E, 2-year EFS and OS were 69.5% (CI 95 61.1-79.1) and 88.1% (CI 95 82-94.7). In MER, 2-year EFS and OS were 71.6% (CI 95 67.7-76.8) and 82.3% (CI 95 79.3-85.3). Compared to PET2-ve, PET2+ve pts had significantly inferior EFS in both MC078E (HR 4.0, CI 95 2.1-7.88, p<0.0001, figure 1a) and MER (HR 2.9, CI 95 1.9-4.1, p<0.0001, figure 1c). Compared to PET2-ve , PET2+ve pts had a trend towards lower OS in MC078E (HR 2.0, CI 95 0.9-4.9, p=0.1, figure 1b) and a significantly lower OS in MER (HR 2.3, CI 95: 1.5-3.4, p<0.0001, figure 1d). In subgroup analysis of MC078E, PET2+ve pts had lower EFS and a trend towards lower OS in all subgroups except IPI 0-2 (Table 1). In MER, PET2+ve pts had lower EFS and OS in all the subgroups except stage I-II and IPI 0-2 (Table 1).
Conclusions: Positive PET2 was associated with increased risk of disease progression and death in newly diagnosed DLBCL. Results of our study provide robust evidence of importance of PET2 as an early predictor DLBCL pts at high risk of progression in two independent prospective cohorts. PET2-guided risk-adapted strategies using chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy and bispecific antibodies may potentially improve outcomes, should be explored in clinical trials and results of our study serve as a benchmark for such studies.
Maurer: Kite Pharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Genentech: Research Funding; Morphosys: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Nanostring: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Wang: Genentech: Research Funding; Eli Lilly: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Research Funding; MorphoSys: Research Funding; InnoCare: Research Funding; Incyte: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; LOXO Oncology: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Cerhan: Celgene/BMS: Other: Connect Lymphoma Scientific Steering Committee, Research Funding; Regeneron Genetics Center: Other: Research Collaboration; NanoString: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding. Ansell: Bristol Myers Squibb, ADC Therapeutics, Seattle Genetics, Regeneron, Affimed, AI Therapeutics, Pfizer, Trillium and Takeda: Research Funding. Habermann: Seagen: Other: Data Monitoring Committee; Incyte: Other: Scientific Advisory Board; Tess Therapeutics: Other: Data Monitoring Committee; Morphosys: Other: Scientific Advisory Board; Loxo Oncology: Other: Scientific Advisory Board; Eli Lilly & Co.,: Other: Scientific Advisor. Witzig: Celgene/BMS, Acerta Pharma, Kura Oncology, Acrotech Biopharma, Karyopharm Therapeutics: Research Funding; Karyopharm Therapeutics, Celgene/BMS, Incyte, Epizyme: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Nowakowski: Celgene, NanoString Technologies, MorphoSys: Research Funding; Celgene, MorphoSys, Genentech, Selvita, Debiopharm Group, Kite/Gilead: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal